
To Book an Appointment
Call Us+91 954 002 5025To Book an Appointment
Call Us+91 954 002 5025Understanding Blood Cancer & Its Symptoms
By Medical Expert Team
Oct 17 , 2023 | 7 min read
4
Your Clap has been added.
Thanks for your consideration
Share
Share Link has been copied to the clipboard.
Here is the link https://www.blkmaxhospital.com/blogs/blood-cancer-symptoms
Understanding Blood Cancer & Its Early Signs
Blood cancer, or hematologic cancer, occurs when blood cells grow uncontrollably, interfering with the body's ability to fight infection and manage bleeding. These cancers typically begin in the bone marrow or the lymphatic system. While a diagnosis can be overwhelming, understanding the symptoms of blood cancer is the first step toward early intervention and improved clinical outcomes.
In 2020, over 1.3 million cases were reported globally. In India, the burden of blood cancers in elderly and pediatric populations is rising, making it vital to recognize leukemia symptoms, lymphoma, and myeloma early on. Identifying blood cancer symptoms in English, Hindi (blood cancer ke lakshan), and local languages is the first line of defense in modern oncology.
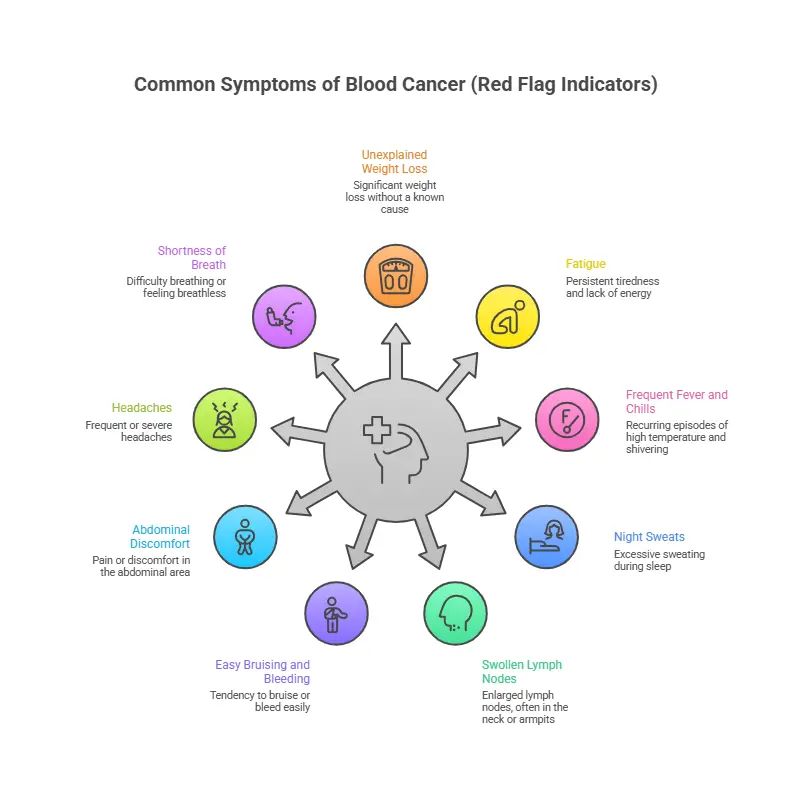
Common Symptoms of Blood Cancer (Red Flag Indicators)
While blood cancers types vary, patients often report several "red flag" indicators. If you notice these signs of blood cancer, a cancer screening or a Complete Blood Count (CBC) test is recommended.
- Unexplained Weight Loss: Rapid, unintended weight loss (losing 10% of body weight in 6 months) is a significant sign of blood cancer.
- Fatigue: Persistent exhaustion that doesn't improve with rest is often due to anemia, a common symptom of leukemia in female and male patients.
- Frequent Fever and Chills: Recurrent infections or low-grade blood cancer ke lakshan like persistent fever may indicate a weakened immune system.
- Night Sweats: Drenching sweats that soak through clothes are common lymphoma leukemia symptoms.
- Swollen Lymph Nodes: A cancer of lymph node usually presents as a painless lump in the neck, armpit, or groin.
- Easy Bruising and Bleeding: Low platelet counts can cause nosebleeds or blood cancer skin symptoms like tiny red spots (petechiae).
- Abdominal Discomfort: An enlarged spleen may cause a feeling of fullness or blood cancer vomiting after eating small amounts.
- Headaches: Headaches can happen when there's higher pressure inside the skull, which is called intracranial hypertension. This can be due to blood cancer affecting the central nervous system or causing inflammation due to increased white blood cell counts.
- Shortness of Breath: Shortness of breath can result from anemia or the enlargement of lymph nodes or organs due to blood cancer. When the body's ability to carry oxygen decreases, people might feel short of breath, even with minor physical effort.
What Causes Blood Cancer? Risk Factors & Prevention
While the exact cause is often genetic mutations in DNA, certain factors increase the risk of developing blood cancers. These include exposure to high-level radiation, certain chemicals like benzene, and a family history of hematologic malignancies. For the blood cancers in elderly populations, age-related cellular changes play a significant role. Prevention focuses on avoiding known carcinogens and undergoing regular cancer screening if you are in a high-risk category.
Know more about - 7 Myths and Facts about Blood Cancer.
Blood Cancer Symptoms by Type
1. Leukemia Symptoms
Leukemia symptoms in adults and children occur when the bone marrow produces too many abnormal white blood cells.
1.1. Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL)
A fast-progressing subtype. Children with ALL may experience bone and joint pain, persistent fatigue, and increased susceptibility to infections. ALL impairs normal blood clotting and may manifest as pale skin.
1.2. Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML)
Characterized by rapid growth of myeloid cells. Common signs include swollen gum symptoms (leukemic infiltration) and a 15000 WBC count or higher on tests. AML can also cause rapid, unintentional weight loss.
1.3. Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL)
A slowly progressing cancer. Most patients are diagnosed at a low stage during routine tests. Symptoms include easy bruising and recurrent infections like pneumonia.
Learn more about - Top 5 Symptoms of Pneumonia You Should Not Ignore.
1.4. Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CML)
Typically presents with massive spleen enlargement (splenomegaly), causing a dragging sensation in the abdomen. Patients may also notice a high 8.7 MPV blood test result.
2. Childhood Leukemia: Recognizing the Specific Signs
Childhood Leukemia can manifest differently than in adults. Recognizing these signs is crucial:
- Behavioral Changes: Decreased interest in activities or social withdrawal.
- Pale or 'Washed-out' Skin: A common sign due to anemia.
- Testicular Swelling: In some cases, leukemia symptoms include swelling of the testicles in male children.
- Severe Tiredness: Lack of energy even after rest.
3. Lymphoma Symptoms
Lymphoma originates in the lymphatic system and is divided into:
- Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma (NHL): Hallmarked by enlarged lymph nodes, chest pain, and pruritus (severe itching). NHL follows "Classical B symptoms": fever, weight loss, and night sweats.
- Hodgkin Lymphoma (HL): Characterized by Reed-Sternberg cells. HL typically spreads in an orderly manner from one group of lymph nodes to the next.
4. Myeloma Symptoms
Develops in plasma B cells.
- Hypercalcemia: Can cancer cause high potassium or calcium? Yes, Multiple Myeloma causes high calcium levels, leading to constipation and confusion.
- Kidney Damage: Myeloma proteins can lead to increased thirst and swelling in the extremities.
- Peripheral Neuropathy: Tingling or pain in hands and feet.
5. Myelodysplastic Syndromes (MDS) & Myeloproliferative Neoplasms (MPN)
- MDS Symptoms: Dysfunction in bone marrow leading to pancytopenia. Women with MDS may experience heavy or prolonged menstrual bleeding.
- MPN Symptoms: Overproduction of blood cells. Polycythemia Vera leads to thickened blood (hyperviscosity syndrome) and visible distension of veins in the head and neck.
Read more about - What is Cancer and Its Different Types?
Diagnostic Criteria: Lab Markers and Clinical Findings
To move from "signs of blood cancer" to a formal diagnosis, doctors look for specific clinical markers. It is important to note that diagnostic tests such as PET-CT scans or bone marrow biopsies involve significant costs and should only be performed under medical supervision.
|
Diagnostic Marker |
Normal Range |
Potential Blood Cancer Indicator |
|
White Blood Cell (WBC) Count |
4,500 - 11,000/mcL |
15000 WBC count or higher (Potential Leukemia indicator) |
|
Mean Platelet Volume (MPV) |
7.5 - 11.5 fL |
Abnormal 8.7 MPV blood test (can vary by cancer type) |
|
B12 Levels |
200 - 900 pg/mL |
Unexpectedly high B12 (Does high b12 mean cancer? It requires further clinical correlation) |
|
Potassium Levels |
3.6 - 5.2 mmol/L |
Elevated (Can cancer cause high potassium? Yes, via tumor lysis) |
Stages of Blood Cancer
Unlike solid tumors, the 2nd stage of blood cancer or blood cancer 2nd stage symptoms are defined differently because blood is fluid.
- 1st stage blood cancer symptoms: Usually localized to lymph nodes or a slight increase in cell counts. 1st stage blood cancer treatment often involves watchful waiting, targeted therapy or localized radiation.
- Second stage of blood cancer symptoms: Often involves enlargement of the liver or spleen (blood cancer 2nd stage symptoms).
- Advanced Stages: Involvement of bone marrow and multiple organ systems.
If you experience sudden, severe blood cancer vomiting, a fever above 103°F that won't break, or petechiae (blood cancer symptoms on skin) that spread rapidly, seek emergency care immediately. These can be signs of acute leukemia or severe infection.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are the 1st stage of blood cancer symptoms?
Early signs, or 1st stage blood cancer symptoms, often include persistent fatigue, unexplained fever, and painless swelling of the lymph nodes. Unlike other cancers, blood cancer is often staged by cell count and organ involvement (like the spleen) rather than a singular tumor.
2. Does high B12 mean cancer?
Not necessarily. While some studies ask "does high b12 mean cancer" because it can correlate with certain myeloid leukemias, high B12 is frequently caused by liver disease, supplement use, or kidney issues. A doctor must evaluate this alongside a CBC to rule out solid tumors or hematologic malignancies.
3. What are common blood cancer skin symptoms?
Blood cancer symptoms on skin include petechiae (tiny red/purple spots), easy bruising, or a pale appearance due to anemia. Pruritus (itching) is also a significant sign of blood cancer, specifically in certain lymphomas.
4. Can a 15000 WBC count indicate leukemia?
A 15000 WBC count is elevated (leukocytosis). While it often indicates a simple infection, if it remains high and is accompanied by a sign of blood cancer like night sweats or bone pain, it requires a hematologist's review to rule out leukemia.
5. What are the symptoms of blood cancer in male patients vs. females?
Symptoms of blood cancer in male patients can include testicular swelling in certain lymphomas. Conversely, woman blood cancer symptoms may manifest as unusually heavy menstrual bleeding (due to low platelets) or severe anemia-related weakness (symptoms of leukemia in female).
6. What are the signs of blood cancer?
Common signs include persistent fatigue, drenching night sweats, unexplained weight loss, and painless swelling of lymph nodes in the neck or armpit.
Learn more about - 7 Most Common Signs of Breast Cancer in Women.
7. What is the 1st stage blood cancer treatment?
Treatment for early-stage blood cancer depends on the type but often involves stem cell transplantation, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, Immunotherapies, targeted therapies, or a "watchful waiting" approach in chronic cases.
Disclaimer: The information provided in this blog is for educational purposes only and does not substitute professional medical advice. If you are experiencing signs of blood cancer or persistent blood cancers symptoms, please consult a specialist immediately for a formal cancer screening. The decision to undergo specific diagnostic tests or treatments of cancer should be made in consultation with a qualified oncologist, as these involve financial and health commitments.
References
[1] Sung, H., Ferlay, J., Siegel, R. L., Laversanne, M., Soerjomataram, I., Jemal, A., & Bray, F. (2021). Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians, 71(3), 209–249. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33538338/
[2] American Cancer Society. (2023). Signs and Symptoms of Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma. https://www.cancer.org/cancer/non-hodgkin-lymphoma/detection-diagnosis-staging/signs-symptoms.html
[3] Howard, S. C., Jones, D. P., & Pui, C. H. (2011). The Tumor Lysis Syndrome. New England Journal of Medicine, 364(19), 1844–1854. https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMra0904569
[4] American Cancer Society. (2024). Hypercalcemia in Cancer patients. https://www.cancer.org/treatment/treatments-and-side-effects/physical-side-effects/high-blood-calcium.html
[5] Arendt, J. F., & Nexo, E. (2013). Unexpected high plasma vitamin B12: a critical review. Clinical Chemistry and Laboratory Medicine (CCLM). https://www.degruyter.com/document/doi/10.1515/cclm-2012-0545/html
[6] National Cancer Institute. (2023). Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Treatment. https://www.cancer.gov/types/leukemia/patient/cll-treatment-pdq

Written and Verified by:
Medical Expert Team
Related Blogs

Medical Expert Team
Feb 05 , 2019 | 4 min read

Medical Expert Team
Feb 22 , 2019 | 2 min read
Most read Blogs
Get a Call Back
Related Blogs

Medical Expert Team
Feb 05 , 2019 | 4 min read

Medical Expert Team
Feb 22 , 2019 | 2 min read
Most read Blogs
- Cancer Centre
- Centre For Bone Marrow Transplant
- Heart & Vascular Institute
- Centre For Neurosciences
- Institute For Digestive & Liver Diseases
- Centre For Renal Sciences & Kidney Transplant
- Institute For Bone, Joint Replacement, Orthopedics
Spine & Sports Medicine - Centre For Chest & Respiratory Diseases
- Centre For Plastic & Cosmetic Surgery
- Centre For Child Health
- Centre for Women Health
- Centre For Diabetes, Thyroid, Obesity & Endocrinology
- Centre for Critical Care
- Oncology
- Cardiology and Heart Surgery
- Neurology and Neurosurgery
- Haematology & BMT
- Orthopaedics & Spine Surgery
- Arthroscopy & Sports Medicine Centre
- Nephrology, Urology and Kidney Transplant
- Liver Transplantation
- Gastroenterology and Hepatology
- Gastrointestinal Surgery
- General & Minimal Access Surgery
- Gynaecology & Obstetrics
- ENT & Cochlear Implant
- Internal Medicine
- Orthopaedic Doctor in Delhi
- Oncologist in Delhi
- Cardiologist/Cardiac Surgeon in Delhi
- Gyne-Oncologist in Delhi
- Pulmonologist in Delhi
- Nephrologist in Delhi
- General Surgeon in Delhi
- Gastroenterologist in Delhi
- Endocrinologist in Delhi
- Breast Cancer Specialist in Delhi
- Kidney Specialist in Delhi
- Urologist in Delhi
- Neurologist/Neuro Surgeon in Delhi
- Liver Transplant Surgeon in Delhi





